- Home
- About us
- Products
- FC Type Telescopic Cylinders
- FE Type Telescopic Cylinders
- FEE Type Telescopic Cylinders
- Under Body Tipping Cylinders
- Telescopic Cylinders For America market
- 7 Ton and 12 Ton Telescopic Cylinders
- Agricultural Trailer 2 and 3 Stage Tipping Rams
- Dump Trailer Cylinder
- Hydraulic Crutch
- Waste Compactor Hydraulic Cylinder
- Double Acting Telescopic Cylinders
- Bushing Mounting Cylinder
- Clevis Mounting Hydraulic Cylinder
- Snow Plow Hydraulic Cylinders
- Agricultural Hydraulic Cylinders
- Custom Hydraulic cylinder
- Heavy Duty Metallurgical Oil Cylinder
- Engineering Hydraulic Cylinder
- Log Splitter Hydraulic Cylinder
- Tie Rod Hydraulic Cylinder
- Hydraulic Cylinder For Brick Machine
- Agricultural Telescopic Cylinders For Europe market
- Piston Rod
- Cold Drawn and SRB/Hone Tube
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
Seals for Hydraulic Cylinders
sourceHydraulic & Pneumatic
time2020/01/07
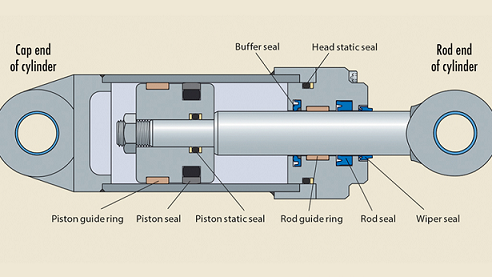
- Pressure has been mounting to design and produce cylinders that offer superior sealing performance for enhanced reliability. This article provides an overview of hydraulic cylinders along with the various types of hydraulic seals for specification.
Seals for Hydraulic Cylinders
The type of cylinder and the application which it is used for are two of the main criteria when selecting the appropriate seals and guides. Applications are referred to as light-duty, medium-duty, or heavy-duty applications. The duty levels are typically characterized by the following criteria:
Light-duty cylinders are used for stationary equipment in a factory environment and are characterized by system pressures up to 160 bar (2,300 psi) and temperatures up to 70°C (160°F).
Medium-duty cylinders often are used in agriculture off-highway equipment with system pressures up to 250 bar (3,625 psi) and temperatures up to 90°C (195°F).
Heavy-duty cylinders are found in off-highway earthmoving, mining, and forestry equipment and are characterized by system pressures to 400 bar (5,800 psi) or greater and with temperatures exceeding 90°C (195°F), and perhaps intermittently to 110°C (230°F).
Hydraulic Cylinder seals
Hydraulic cylinder seals are used to seal the opening between various components in the hydraulic cylinder. They are designed to retain hydraulic fluids, exclude solid or liquid contaminants, and maintain hydraulic pressure. These tasks require a variety of different seal designs and performance-enhancing features. Seal material must conform to irregularities in metal surfaces to block fluid passage. To adjust to clearance gap size changes, the seal must expand or compress rapidly to follow dimensional variations. Finally, to resist being extruded into gaps, the seal must have sufficient modulus and hardness to withstand shear stress produced by system pressure.
Successful sealing involves containment of fluid within fluid power systems and components while excluding contaminants. The surfaces in contact with a seal determine what type to use. The surface can either be static or dynamic—in motion or without movement. Static seals are typically used when there is no relative motion between mating surfaces. Dynamic seals are the opposite. They are used when there is motion between surfaces. This can be either reciprocating or oscillating motions.
Rod and Buffer Seals
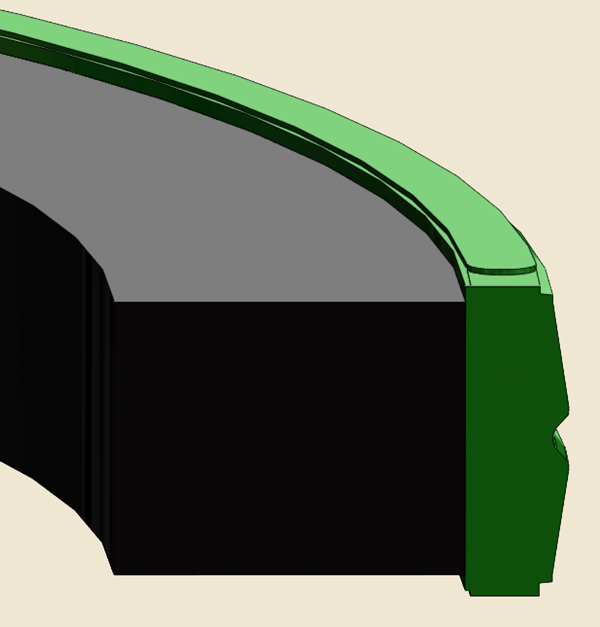
Rod and buffer seals maintain sealing contact with a sliding motion between the cylinder head and the piston rod. Depending on the application, a rod sealing system can consist of a rod seal and a buffer seal or a rod seal only. Rod sealing systems for heavy-duty applications typically consist of a combination of both seal types. The buffer seal is arranged between the rod seal and the piston in the cylinder head.
Rod seals act as a pressure barrier to keep the operating fluid inside the cylinder. They also provide a thin lubrication film on the piston rod that lubricates the rod seals and wiper seals. The lubricant also inhibits corrosion of the piston rod surface. However, the lubrication film must be thin enough so it returns internal to the cylinder during the return stroke. Selecting profiles and materials for a rod sealing system is a complex task, considering all possible cylinder designs and application criteria. Rod and buffer seals come in many different profiles and in a wide range of materials, series, and sizes to perform under a variety of operating conditions and applications.
Buffer seals protect rod seals by reducing the magnitude of pressure peaks. Abrupt pressure peaks can occur by external forces acting on the piston rod, initiated by the fluid inside the cylinder and create higher fluid pressures in the cylinder. These pressure peaks can be in excess of the system operating pressure. Buffer seals—in combination with rod seals—provide an effective rod sealing system for cylinders in heavy-duty applications at high temperatures and pressures.
Piston Seals
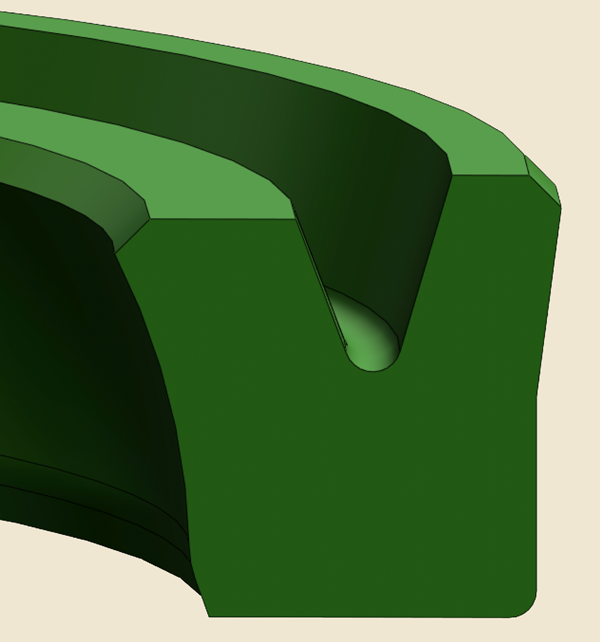
Piston seals maintain sealing contact between the piston and the cylinder bore. Differential pressures acting on the piston to extend or retract the piston rod can exceed 400 bar (5,800 psi). The pressure acting on the piston seal increases contact forces between the piston seal and cylinder surface. Therefore, the surface properties of the sealing surfaces are critical to proper seal performance.
Piston seals serve as a pressure barrier and prevent fluid from passing the piston, which is important for controlling the cylinder motion or maintaining the position when at rest. Piston seals are typically classified into single-acting (pressure acting on one side only) and double-acting (pressure acting on both sides) seals.
Double-acting piston seals have a symmetrical profile and identical sealing functions in both directions. Typically, double-acting piston seals consist of a slide ring and an energizer. Because double-acting cylinders contain fluid on both sides of the piston, a relatively thick lubrication film can be permitted between the piston seal and the cylinder bore to minimize friction and wear.
A single-acting piston seal is designed for cylinders where pressure is applied from one side only. The piston in single-acting cylinders may have oil on the pressure side only, while the opposite side is open to atmosphere. Therefore, the piston seal must leave minimal oil film when passing along the cylinder bore since the transportation of oil otherwise would result in a leakage to the exterior.
In single-acting cylinders, the open end may push air out and draw air in as the piston reciprocates. This air may carry moisture and contaminants into the cylinder, which can lead to seal damage. Vent filters can be fitted to the open side of the cylinder to reduce contaminants entering the inside of the cylinder. The cylinder bore may also be hard chromium plated to prevent corrosion.
Wiper Seals
Hydraulic cylinders operate in a variety of applications and environmental conditions, including exposure to dust, debris, or outside weather conditions. To prevent these contaminants from entering the cylinder assembly and hydraulic system, wiper seals (also known as scrapers, excluders, or dust seals) are fitted on the external side of the cylinder head.
Wiper seals maintain sealing contact to the piston rod when the equipment is stationary (static, no reciprocating motion of rod) and in use (dynamic, reciprocating rod). Without a wiper seal, the retracting piston rod could transport contaminants into the cylinder.
Guide Lubrication & Guide Rings
Rod guides are typically placed inward of both the rod and buffer seal and should be lubricated on assembly with the same medium as used in the system. The guide must receive ample lubrication at all times and should not be outside the rod seal. However, in certain conditions, guides with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) added may be used outside the rod seal due to their self-lubricating properties.
Guide rings provide effective guidance of components that are in relative motion to each other and accommodate radial loads acting on the cylinder assembly. The selection of the right seal and guide for a given application requires consideration of many factors. Rod and piston guide rings prevent metal-to-metal contact between components, react to the radial load caused by side loads on the cylinder assembly, and keep the piston rod and piston radially centered in the cylinder assembly within acceptable limits for the seals. These functions are important for performance of the rod sealing system and piston sealing system.
Sealing Material Selection is Key
Industrial seals are exposed to a wide range of challenging operating conditions such as high temperature, speed, pressure, and aggressive chemicals. To handle these and other harsh conditions, it is essential to select the most suitable sealing materials. Several factors impact material selection, including exposure to media, pressure, temperature, and potentially stringent regulatory requirements common in food and beverage or oil and gas applications. Types of sealing materials include:
Rubbers—NBR, FKM, and HNBR are commonly used rubber materials in hydraulic applications. They are extremely flexible and can be stretched and deflected by exerting relatively little force. Many of them deliver excellent resistance to mineral oils, greases, or other media.
Thermoplastic elastomers—These offers advantages typical of both rubber and plastic materials. SKF’s high-performance thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) combine excellent abrasion and wear resistance, low compression set, and high tear strength and outstanding pressure resistance.
PTFE—Engineered to handle extreme conditions, PTFE and its compounds can withstand aggressive chemicals plus high temperatures and pressures. Due to their extremely low coefficients of friction, they can also tolerate dry running conditions.
Plastics—Plastic materials can meet higher temperature, chemical, and mechanical property requirements and can range from engineering plastics to high-performance plastics. Backup rings are typically made of plastics and used to enhance the pressure carrying capability of a rod or piston seal.
Criteria for Seal Specification
Designing sealing and guide systems in hydraulic cylinders requires careful attention to the interaction between all cylinder components and the operating conditions as well as the application requirements. The selection of the right seal profile and material for a given application requires consideration of many factors. For any application factors outside of the ordinary or to specify sealing systems in new hydraulic cylinder designs, a certain amount of expertise may be required.
Before seals can be selected, certain applications, parameters, and information should be collected. The following most common application considerations are almost always required when selecting hydraulic seals:
Fluid pressure range—the range of operating fluid system pressure, as well as frequency and severity of pressure peaks
Temperature range—the range of the fluid and cylinder assembly, both when operating and at rest
Speed—the stroking speed of the reciprocating piston rod
Fluid media—the type and viscosity of fluid used in the system
Hardware dimensions—the rod and bore diameters, seal groove dimensions and gaps (if already specified), cylinder overall length and stroke length, and surface finish specifications (if already specified)
Application of the cylinder—the type of equipment the cylinder will be used on and how the cylinder will operate in the equipment as well as installation, duty cycles, and environmental factors (external temperature or contaminants).
Customized Solutions for Unique Applications
Performance issues in specific applications are not always solved with a standard or catalog range of products. For difficult and constantly evolving fluid sealing applications, seal engineers can develop a customized sealing solution. Development of this custom solution should include failure analysis and system operating conditions investigations, testing according to customer specifications and performance standards as well as technical training.
Hydraulic seals have a crucial impact on system performance in many applications. Factors such as temperatures, speeds, pressures, lubricants, and other application operating conditions can greatly impact seal life. Specifying the right seal helps boost machine performance, optimize operations,, and lower a machine’s total cost of ownership.
